The Latest Advancements in Malaria Diagnosis and Treatment
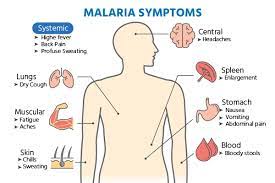
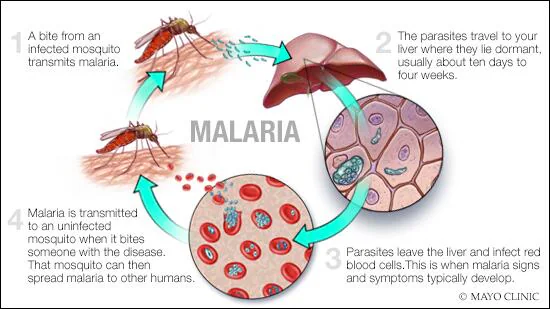
Malaria is a mosquito-borne disease that is caused by a parasite called Plasmodium. It is one of the most common and deadliest diseases in the world, with an estimated 241 million cases and 627,000 deaths in 2020.
There have been significant advances in malaria diagnosis and treatment in recent years. These advances have led to a decrease in the number of malaria deaths, but there is still much work to be done.
Advancements in Malaria Diagnosis
The gold standard for malaria diagnosis is microscopic examination of blood smears. However, this method is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and requires skilled microscopists. In recent years, there have been a number of advances in malaria diagnosis that have made it faster, easier, and more accessible.
One of the most promising advances in malaria diagnosis is the use of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs). RDTs are simple, point-of-care tests that can detect malaria parasites in blood within minutes. RDTs are much faster and easier to use than microscopy, and they can be used by non-specialists.
Another promising advance in malaria diagnosis is the use of molecular diagnostic tests. Molecular diagnostic tests can detect malaria parasites at very low levels, and they can also identify the specific species of malaria parasite. This information is important for choosing the right treatment.
Advancements in Malaria Treatment
The most common treatment for malaria is artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT). ACTs are a combination of two or more drugs that work against the malaria parasite in different ways. ACTs are highly effective against malaria, and they can be used to treat both uncomplicated and severe malaria.
In recent years, there have been a number of advances in malaria treatment. One of the most important advances is the development of new ACTs that are more effective against drug-resistant malaria parasites. Another advance is the development of simplified treatment regimens that are easier to administer and follow.
Future Directions
Despite the advances that have been made in malaria diagnosis and treatment, there is still much work to be done. Malaria remains a major public health problem, and there is a need for new and improved diagnostic tests and treatments.
Some of the future directions in malaria research include:
- The development of new and improved rapid diagnostic tests that are even faster, easier to use, and more affordable.
- The development of new and improved molecular diagnostic tests that can provide more information about the malaria parasite, such as its drug resistance profile.
- The development of new and improved treatments for malaria, including treatments that are effective against drug-resistant parasites.
- The development of new strategies for preventing malaria, such as new vaccines and new methods of vector control.
The advances that have been made in malaria diagnosis and treatment in recent years have saved millions of lives. However, there is still much work to be done. With continued research and development, it is possible to eliminate malaria as a public health problem.