Understanding Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Its Impact on Young Girls in Nigeria
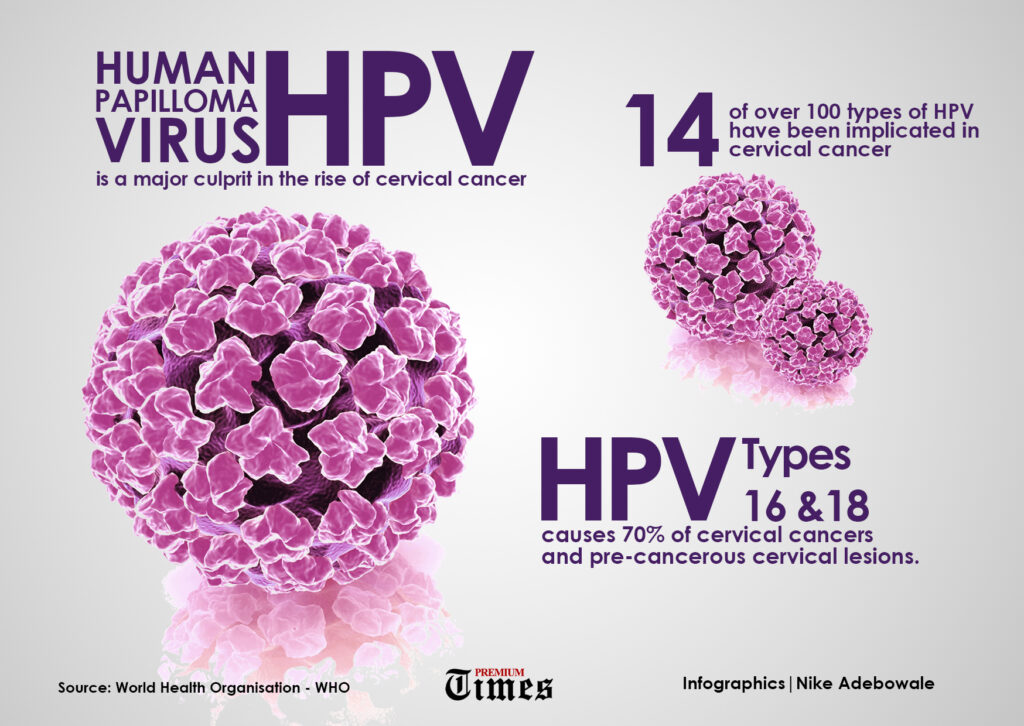
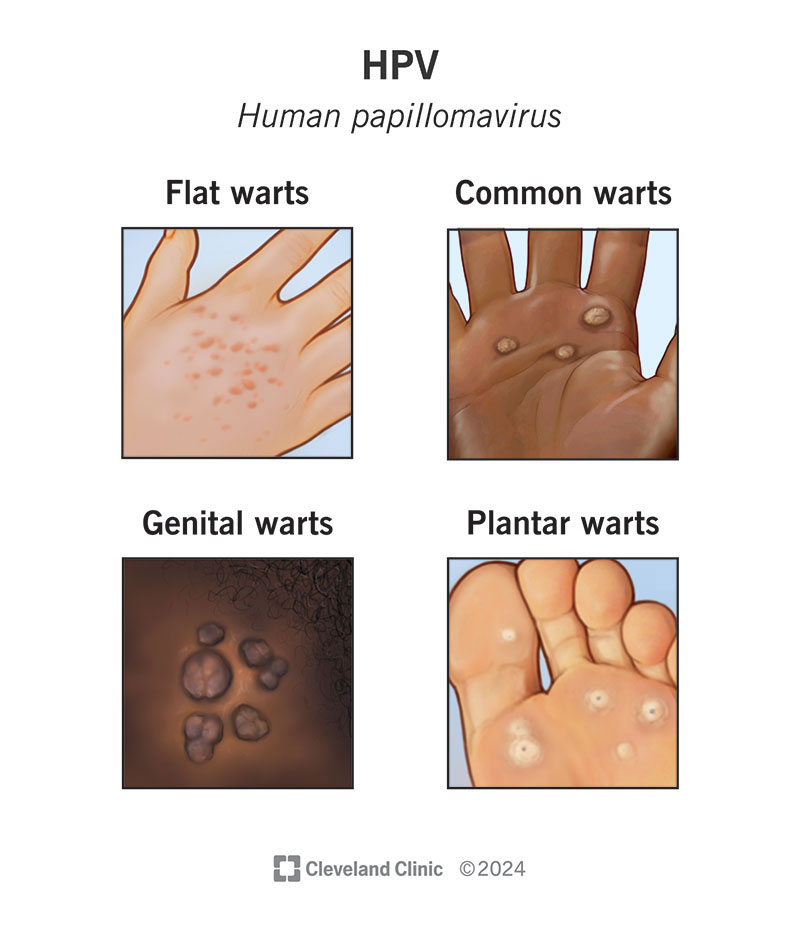
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) is a significant public health concern among young girls in Nigeria. The rising cases of HPV infection and cervical cancer in the country are alarming, highlighting the urgent need for awareness, prevention, and vaccination efforts. Nigeria has a high burden of HPV infection, particularly among young girls and women. The most alarming aspect is the association between HPV and cervical cancer, a disease that is both preventable and treatable if detected early. In Nigeria, a lack of awareness, limited access to healthcare, and cultural factors often contribute to the late diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer. While only a few studies have specifically focused on HPV in Nigeria, the available data sheds light on the prevalence and challenges associated with this virus.
According to a study conducted in Jos, North-Central Nigeria, the prevalence of HPV among adolescent girls was found to be 13.2% 1 . This indicates that a considerable number of young girls are at risk of contracting the virus, which can lead to various health complications, including cervical cancer.
Some risk factors that increase the likelihood of HPV transmission include early sexual activity, having multiple sexual partners, and engaging in unprotected sex 2 . It’s important to note that HPV can be transmitted even with the use of condoms, as the virus can infect areas not covered by the condom. While monogamy and condom use can help reduce the risk of HPV transmission, they do not provide complete protection. HPV can infect areas not covered by condoms, such as the scrotum, vulva, or perineum. Additionally, the virus can also be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact in the genital area, which may not be fully protected by condoms
One of the key factors contributing to the spread of HPV among young girls is low awareness. A study revealed that many parents in Nigeria have a limited understanding of HPV and its associated risks, as well as the availability of HPV vaccines 2 . This lack of awareness acts as a barrier to vaccinating their children and protecting them from the virus.
To address this issue, it is crucial to implement comprehensive awareness campaigns that educate parents, caregivers, and young girls themselves about HPV. These campaigns should focus on raising awareness about the transmission, symptoms, and potential consequences of HPV infection, including the link to cervical cancer.
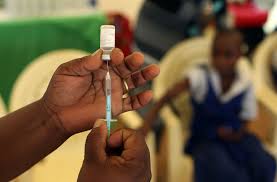
Furthermore, efforts must be made to promote the importance and safety of HPV vaccination. Vaccination is a highly effective preventive measure against HPV infection and can significantly reduce the risk of cervical cancer. However, parental acceptance of HPV vaccination remains a challenge in Nigeria 3 . By disseminating accurate information and addressing concerns related to the vaccine, parents can make informed decisions for the health and well-being of their daughters.
In addition to awareness and vaccination, regular screening and early detection play a vital role in combating HPV and cervical cancer among young girls. Accessible and affordable screening services should be made available across the country, accompanied by education on the importance of regular check-ups.

The vaccine is recommended for children ages 11-12, with two doses given 6 to 12 months apart 1 . However, it can also be given as early as age 9. Vaccinating boys and girls between 9 and 12 years old can prevent more than 90% of HPV cancers when they get older . The vaccine provides cell-mediated immunity and is more effective when taken at a younger age . It’s important for physicians to educate patients about the safety of the vaccine.
To tackle the issue of HPV in Nigeria effectively, collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, educators, and community leaders is crucial. By working together, these stakeholders can implement sustainable strategies that prioritize prevention, education, and healthcare access.
In conclusion, the prevalence of Human Papilloma Virus among young girls in Nigeria is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention. Through comprehensive awareness campaigns, increased parental acceptance of vaccination, and improved access to screening services, we can empower young girls to protect themselves against HPV and reduce the burden of cervical cancer in Nigeria. It is essential to prioritize the health and well-being of our young girls and ensure a brighter, healthier future for them.