Unlocking Sexual Health: A Comprehensive Guide to Erectile Dysfunction for African Men
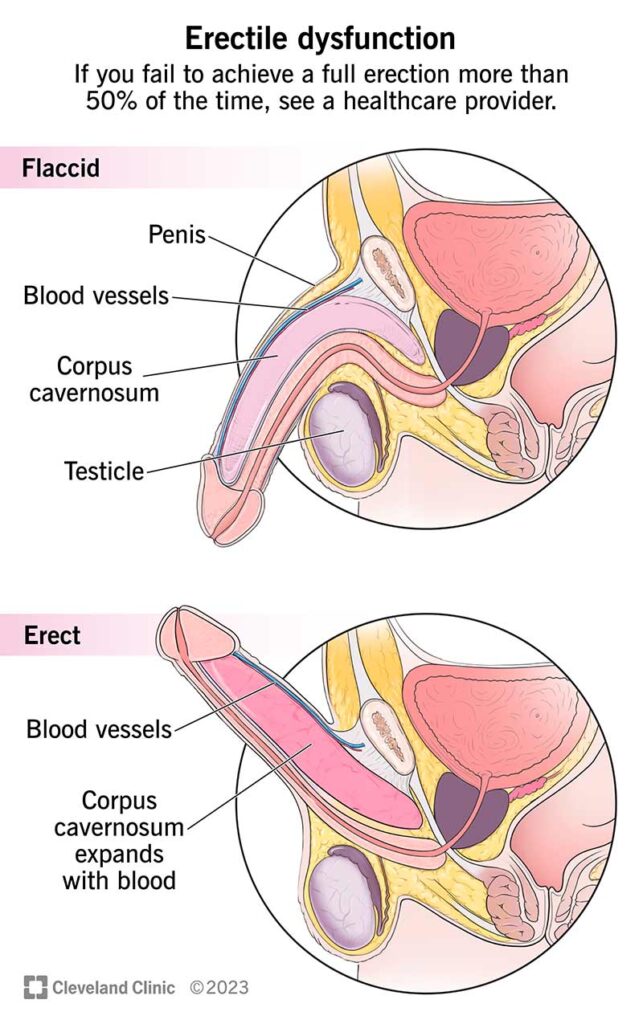
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a common condition affecting men worldwide, irrespective of their ethnic background.

Erectile Dysfunction in African men
However, it’s essential to discuss this condition in the context of African men to address unique factors that may influence its prevalence, causes, treatment, and the broader cultural and societal impact. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of erectile dysfunction as it pertains to African men.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction, often referred to as impotence, is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. While ED can affect men of all ages, it becomes more prevalent with increasing age. Various physical and psychological factors can contribute to this condition. These factors include:
Physical Health: Chronic conditions, particularly those related to cardiovascular health, play a significant role in ED. Here’s a breakdown of the physical health factors:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, which are essential for a healthy erection. This condition, known as diabetic neuropathy, can result in reduced sensitivity and blood flow to the genital area, making it harder to achieve and maintain an erection.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Elevated blood pressure can damage blood vessels throughout the body, including those responsible for carrying blood to the penis. This can reduce blood flow to the penile area, making it difficult to achieve an erection.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Conditions like atherosclerosis, which involves the narrowing of blood vessels due to the buildup of fatty deposits, can impede blood flow, affecting the ability to achieve and sustain an erection.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is often associated with metabolic changes that can lead to hormonal imbalances and increased inflammation. These factors can contribute to ED by affecting blood flow and hormonal function.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions that impact the nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injuries, can disrupt the transmission of nerve signals involved in the erectile response, leading to difficulties in achieving an erection.
Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices can significantly contribute to ED. Here are the key factors:
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, reduces blood flow, and leads to the constriction of arteries. This can hinder the ability to achieve an erection, as adequate blood flow to the penile area is essential for the process.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can lead to alcohol-induced erectile dysfunction. Alcohol acts as a depressant on the nervous system and can affect the ability to maintain an erection.
- Drug Use: Illicit drug use, including substances like cocaine, can have a direct impact on erectile function. These drugs can constrict blood vessels and disrupt the body’s natural processes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and exercise can contribute to obesity and worsen underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, which are risk factors for ED.
Psychological Factors: Mental health plays a substantial role in erectile function:
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to the release of stress hormones, which can have a vasoconstrictive effect, narrowing blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the penis. This can impede the ability to achieve an erection.
- Anxiety: Performance anxiety, related to concerns about sexual performance or pressure to satisfy a partner, can result in heightened stress levels and contribute to ED.
- Depression: Depression can lead to a reduced interest in sexual activities, a lack of motivation, and difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Relationship Issues: Conflicts or problems within a relationship, whether related to communication or emotional intimacy, can lead to stress and anxiety, ultimately affecting sexual performance.
Medications: Some medications can have side effects that impact erectile function:
- Antihypertensive Medications: Some medications prescribed for high blood pressure can have side effects that affect erectile function. Beta-blockers and diuretics are examples of medications that may contribute to ED.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressant drugs, especially selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can lead to sexual side effects, including difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal factors are a significant contributor to ED:
- Testosterone: A drop in testosterone levels, often associated with ageing, can lead to decreased sexual desire and erectile difficulties. Low testosterone levels can affect the nitric oxide pathway, which is essential for achieving an erection.
In summary, Erectile Dysfunction in African men can be influenced by various physical, lifestyle, psychological, medication-related, and hormonal factors. Addressing these factors, whether through lifestyle changes, medical interventions, or psychological support, can significantly improve erectile function and overall sexual health. It’s crucial for individuals experiencing ED to consult with healthcare professionals to identify the underlying causes and explore appropriate treatment option
Prevalence in Africa
In Africa, as in other parts of the world, ED is a growing concern. While there’s a lack of extensive epidemiological data, several factors are contributing to the prevalence of ED in African men:
- Ageing Population: Africa is experiencing a demographic shift, with a growing elderly population. ED becomes more common with age, so this shift is likely contributing to increased cases of ED.
- Lifestyle Changes: Urbanization and changing dietary habits have led to an increase in conditions like diabetes and obesity, which are risk factors for ED.
- Cultural Stigma: In some African cultures, discussing sexual health issues can be considered taboo or stigmatized. This can lead to underreporting and under diagnosis of ED.
- Access to Healthcare: Limited access to healthcare services in some regions of Africa can result in untreated underlying health conditions that contribute to ED.
Treatment and Management
The good news is that ED is a treatable condition, and African men have access to various treatment options. These options include:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthier lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, smoking cessation, and moderation in alcohol consumption, can significantly improve ED.
- Medications: Oral medications like Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra (vardenafil) are commonly prescribed to manage ED. These medications work by enhancing blood flow to the penis.
- Psychological Counseling: For cases related to anxiety or relationship issues, therapy or counseling can be highly effective.
- Hormone Therapy: In situations where hormonal imbalances are the cause of ED, hormone replacement therapy may be recommended.
- Vacuum Erection Devices: These devices use a vacuum to draw blood into the penis, facilitating an erection. They are non-invasive and can be an option for some men.
- Surgical Interventions: In rare cases, surgical procedures like penile implants may be considered for those who do not respond to other treatments.
Breaking the Stigma
Addressing ED in African communities requires open and informed discussions. Breaking the stigma around sexual health issues is essential to encourage men to seek help when needed. Healthcare providers, community leaders, and educational campaigns play a crucial role in promoting awareness and understanding of ED.
Conclusion
Erectile Dysfunction is a prevalent condition among African men, influenced by various factors such as age, lifestyle, and cultural beliefs. However, with the right information, access to healthcare, and open dialogue, ED can be effectively managed and treated. African men should feel encouraged to seek help, as addressing ED not only improves their quality of life but also strengthens their overall well-being and relationships. It’s vital to remember that ED is a common medical condition, and seeking treatment is a positive step towards a fulfilling and healthy life.



